Difference between revisions of "Research"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''' | |'''ZiXOR: Lightweight network coding for reliable communications in IoT.''' | ||
Indoor IoT communications (ZigBee, BlueTooth) usually suffer from the inference from WiFi networks. We devise a lightweight yet reliable network coding system for indoor IoT communications, which incurs minimized redundancy and does not require change on the off-the-shelf devices. The system is implemented with TelosB/TinyOS nodes and significantly improves the reliability of indoor IoT applications. The erratum for the publication is [http://mobinets.org/research/zixor/erratum.pdf here]. | |||
Publications: [http://mobinets.org/ | Publications: [http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMzA2MjEyNDEyNA==.html youku], [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OZeeqFZM5_E youtube], [http://mobinets.org/research/zixor/poster.pdf poster], [http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7748555/ full paper] | ||
|[[File:zixor.png|thumb|link=]] | |[[File:zixor.png|thumb|link=]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''BDTrans: Big data transfer in low power wireless.''' | |'''BDTrans: Big data transfer in low power wireless.''' | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''' | |'''Edge Deployment for IoT.''' | ||
To support real-time processing for large scale IoT, deploying edge nodes with communication, storage, and computational capability is a promising approach. The deployment of edge nodes is an important and key problem. In this paper, we carefully analyze the impacting factors in IoT environments and identified the key challenges for edge node deployment. We then propose a novel three-phase deployment approach which considers both the IoT node diversity and the environmental wireless diversity. The proposed work aims at | |||
minimizing the number of edge nodes and providing real-time processing service for the IoT network. | |||
Publications: | Publications: [http://mobinets.org/pub/edge-iot.pdf IoTJ] | ||
|[[File:zixor.png|thumb|link=]] | |[[File:zixor.png|thumb|link=]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 09:48, 29 August 2019
Low-power wireless
| ZiXOR: Lightweight network coding for reliable communications in IoT.
Indoor IoT communications (ZigBee, BlueTooth) usually suffer from the inference from WiFi networks. We devise a lightweight yet reliable network coding system for indoor IoT communications, which incurs minimized redundancy and does not require change on the off-the-shelf devices. The system is implemented with TelosB/TinyOS nodes and significantly improves the reliability of indoor IoT applications. The erratum for the publication is here. Publications: youku, youtube, poster, full paper |
|
| BDTrans: Big data transfer in low power wireless.
The wireless applications are becoming more and more data-intensive, leading to a massive requirement on big data transfer such as video data, software update, etc. We devise two general building blocks for big data transfer in LP wireless networks. 1) Accurate sender selection: the most efficient network nodes are selected for data transfer. 2) Fast data transmission protocol: an energy-efficient transmission protocol specifically designed for transferring big data. With the modules, energy efficiency and transmission reliability are significantly improved. |
Edge computing
| Edge Deployment for IoT.
To support real-time processing for large scale IoT, deploying edge nodes with communication, storage, and computational capability is a promising approach. The deployment of edge nodes is an important and key problem. In this paper, we carefully analyze the impacting factors in IoT environments and identified the key challenges for edge node deployment. We then propose a novel three-phase deployment approach which considers both the IoT node diversity and the environmental wireless diversity. The proposed work aims at minimizing the number of edge nodes and providing real-time processing service for the IoT network. Publications: IoTJ |
|
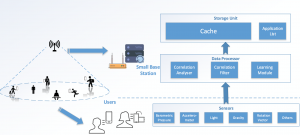
| User Aware Content Caching for Mobile Edge Computing.
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) provides storage, access and computing opportunities for resource-constrained mobile users. In this project, we propose a content caching scheme specifically designed for mobile multimedia users. The mobile users are characterized using the sensory data. Then the potential interest data are predicted according to our prediction of the user preferences. |
Mobile/wearable computing
| ZiXOR: Lightweight network coding for reliable communications in IoT.
Indoor IoT communications (ZigBee, BlueTooth) usually suffer from the inference from WiFi networks. We devise a lightweight yet reliable network coding system for indoor IoT communications, which incurs minimized redundancy and does not require change on the off-the-shelf devices. The system is implemented with TelosB/TinyOS nodes and significantly improves the reliability of indoor IoT applications. The erratum for the publication is here. Publications: youku, youtube, poster, full paper |
|
| BDTrans: Big data transfer in low power wireless.
The wireless applications are becoming more and more data-intensive, leading to a massive requirement on big data transfer such as video data, software update, etc. We devise two general building blocks for big data transfer in LP wireless networks. 1) Accurate sender selection: the most efficient network nodes are selected for data transfer. 2) Fast data transmission protocol: an energy-efficient transmission protocol specifically designed for transferring big data. With the modules, energy efficiency and transmission reliability are significantly improved. |